Pediatric Ophthalmology
Introduction
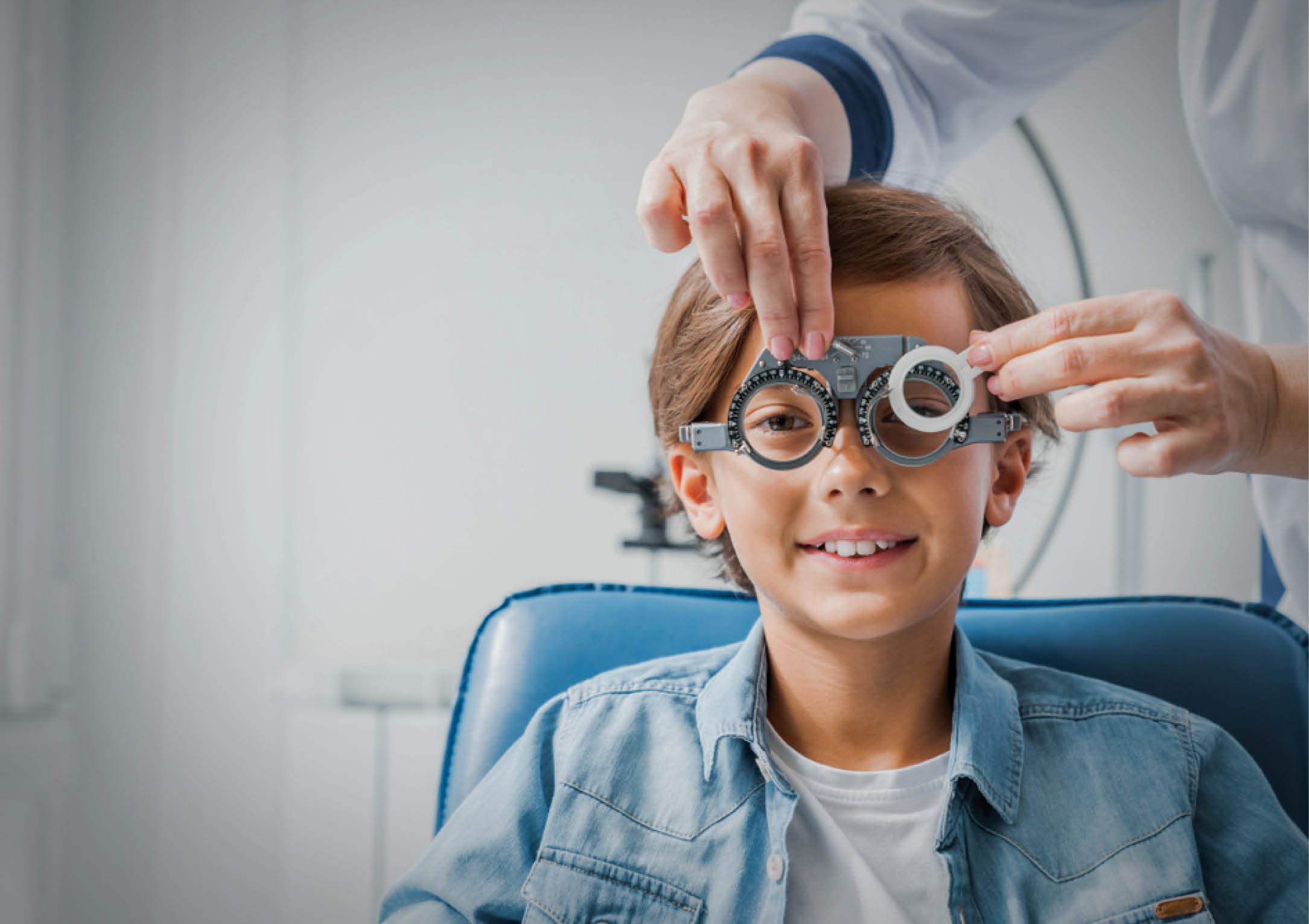
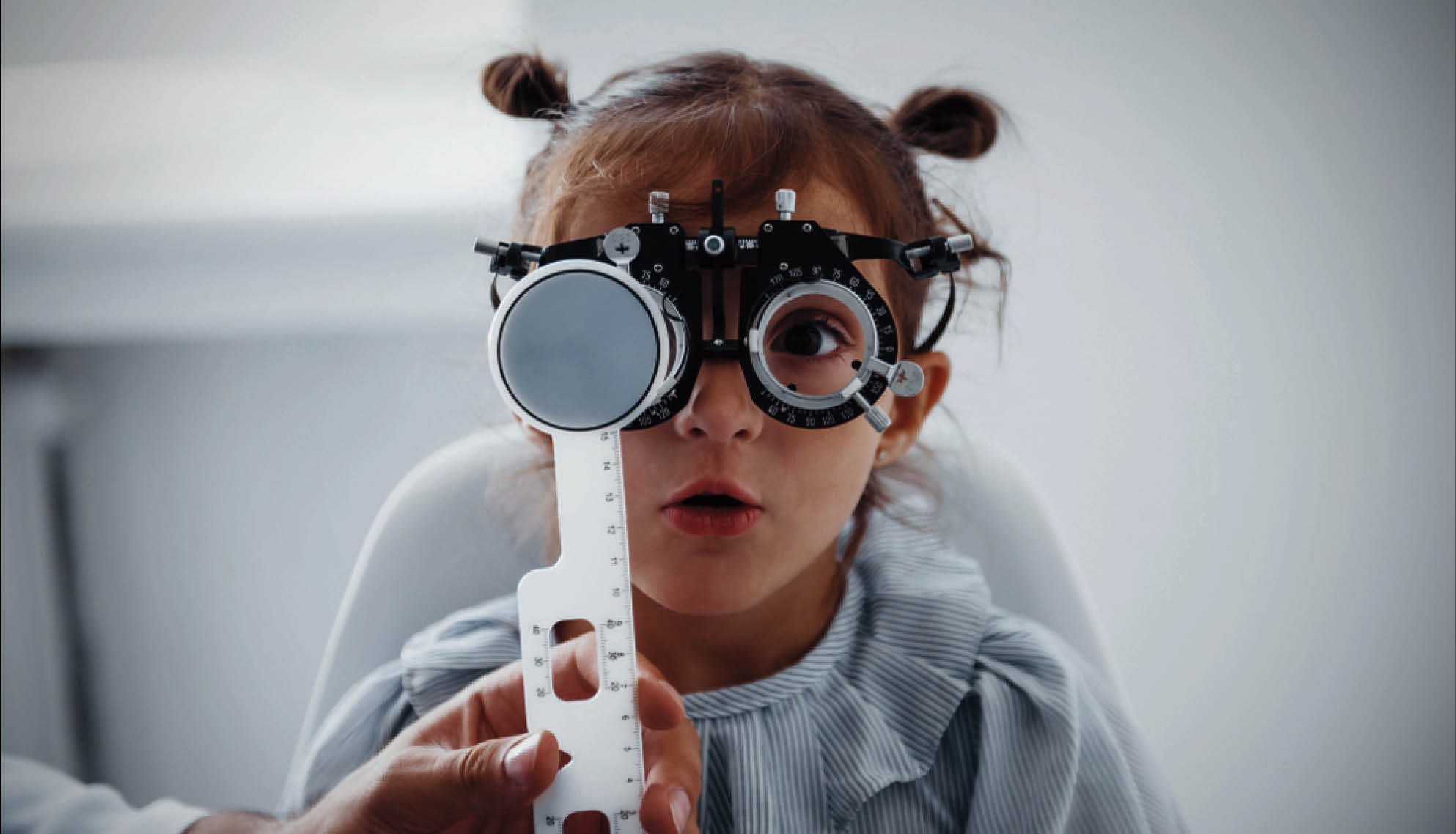
Pediatric Ophthalmology focuses on diagnosing and treating eye conditions in infants, children, and adolescents. Early detection is crucial, as children’s vision develops rapidly in their early years. At Solis Eye Care, we offer specialized care tailored for young patients, ensuring their vision develops correctly and any issues are addressed with care and compassion.
Common Symptoms in Children
Children may not always express vision problems clearly. Look out for:
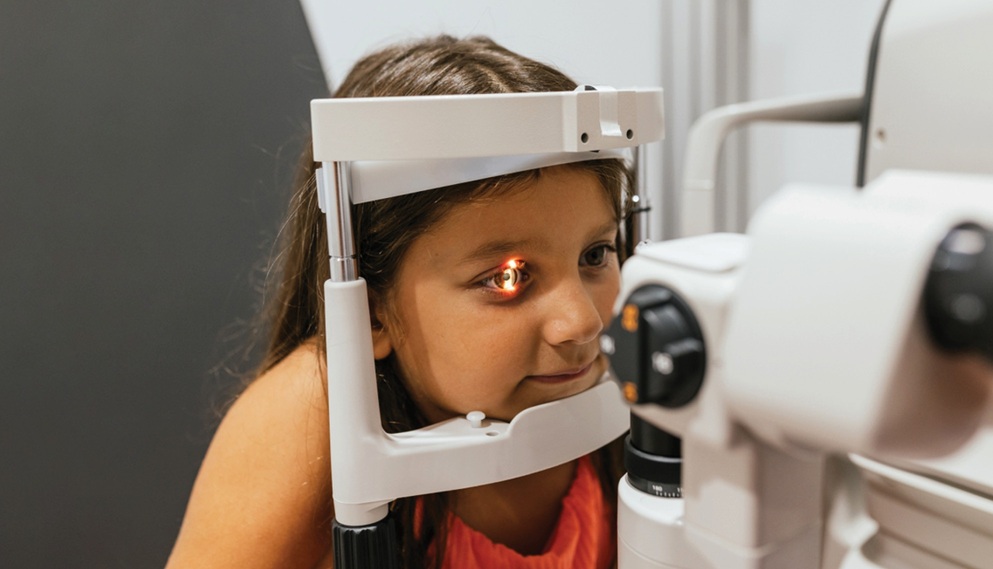

Causes and Risk Factors
- Common Pediatric Eye Conditions
- Diagnosis & Treatment at Solis
- Long-Term Care and Monitoring
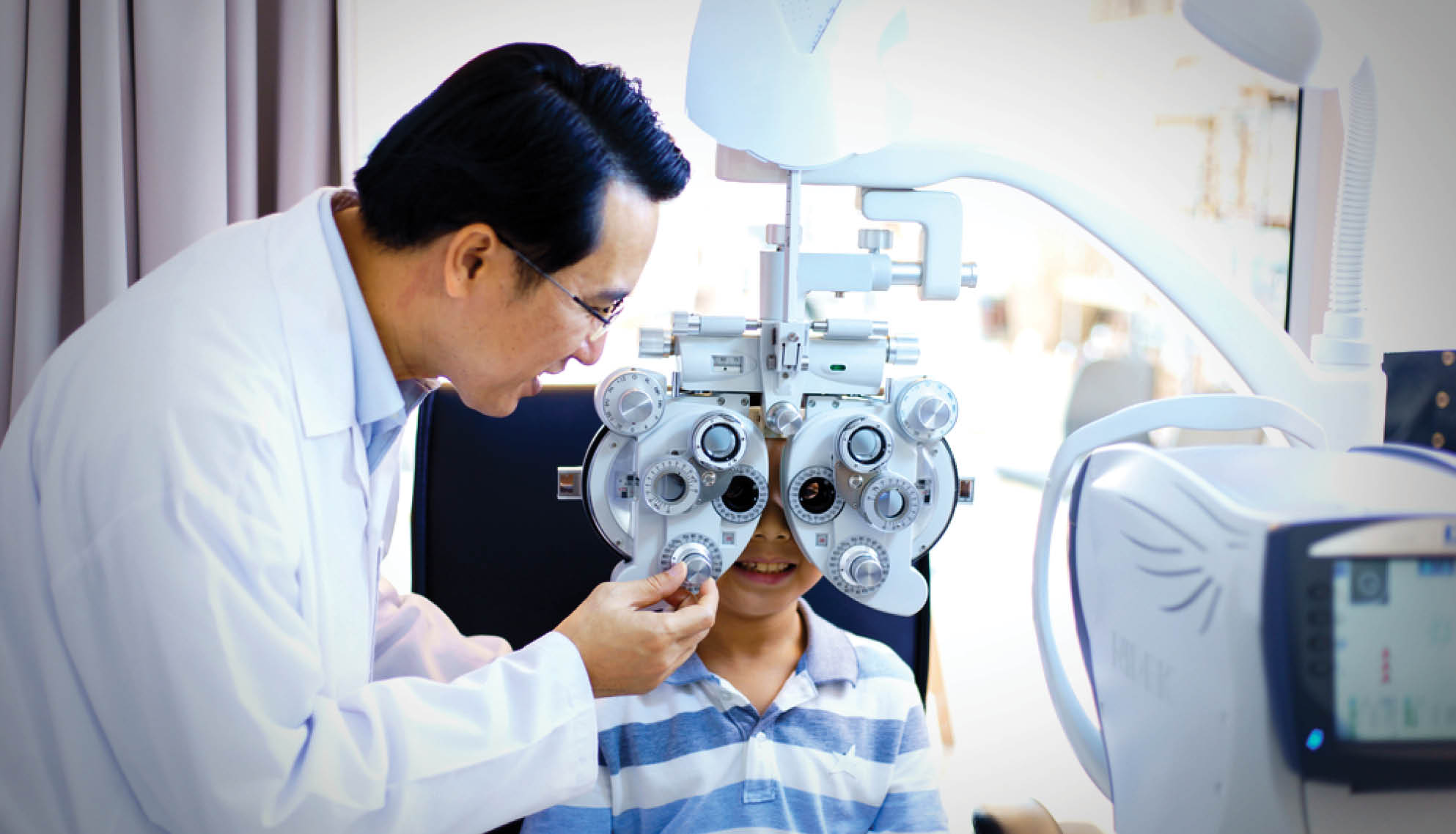
We create a child-friendly environment to make eye exams easy and stress-free. Treatments include:


Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Ideally by 6 months, then at 3 years, and before starting school.
Yes, with glasses, therapy, or surgery depending on the cause.
It may cause strain and increase the risk of myopia. Regular breaks and eye exercises help.
Lazy eye (amblyopia) is weaker vision in one eye. Early treatment improves vision significantly.
Yes, premature babies are at risk of Retinopathy of Prematurity and should be screened early.

