Glaucoma
Introduction
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, often due to increased pressure inside the eye. This damage is irreversible and can lead to permanent vision loss if not treated early. Known as the “silent thief of sight,” glaucoma often has no noticeable symptoms in its early stages but can be effectively managed with timely diagnosis and treatment.
Common Symptoms of Glaucoma
Many people do not experience symptoms until the disease has advanced. Regular eye exams help detect it early.
Gradual Loss of Side Vision
Often unnoticed until significant damage has occurred.
Blurred or Hazy Vision
May worsen over time if untreated.
Eye Pain or Headaches
More common in acute types of glaucoma.
Seeing Halos Around Lights
Especially noticeable in low-light conditions.
Redness in the Eye
A sign of increased eye pressure.
Sudden Vision Loss
In rare, severe cases (acute angle-closure glaucoma).
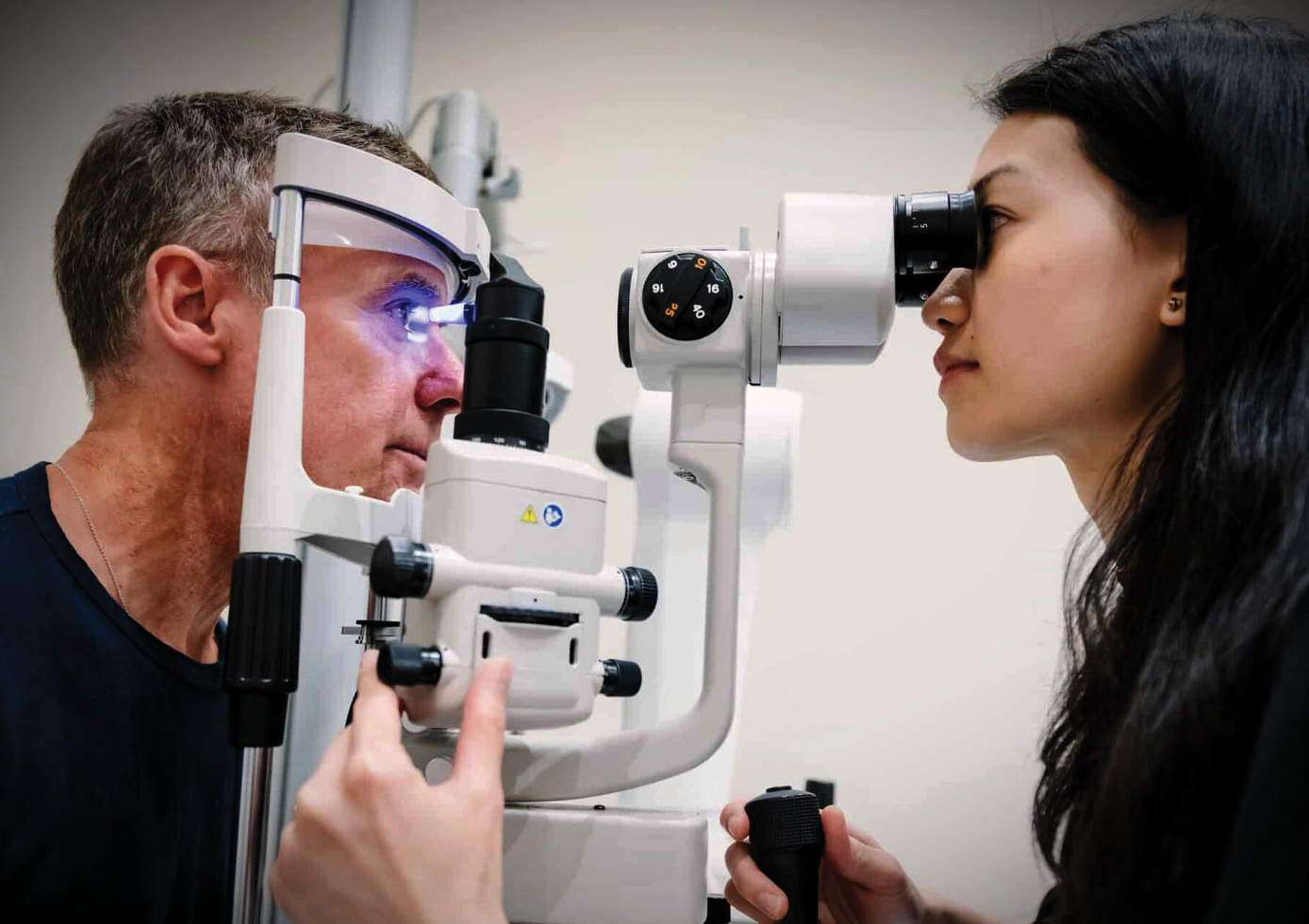
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing glaucoma:
- Types of Glaucoma
- Diagnosis & Treatment at Solis
- Long-Term Care and Monitoring
Glaucoma can be classified into several types based on its cause and presentation:
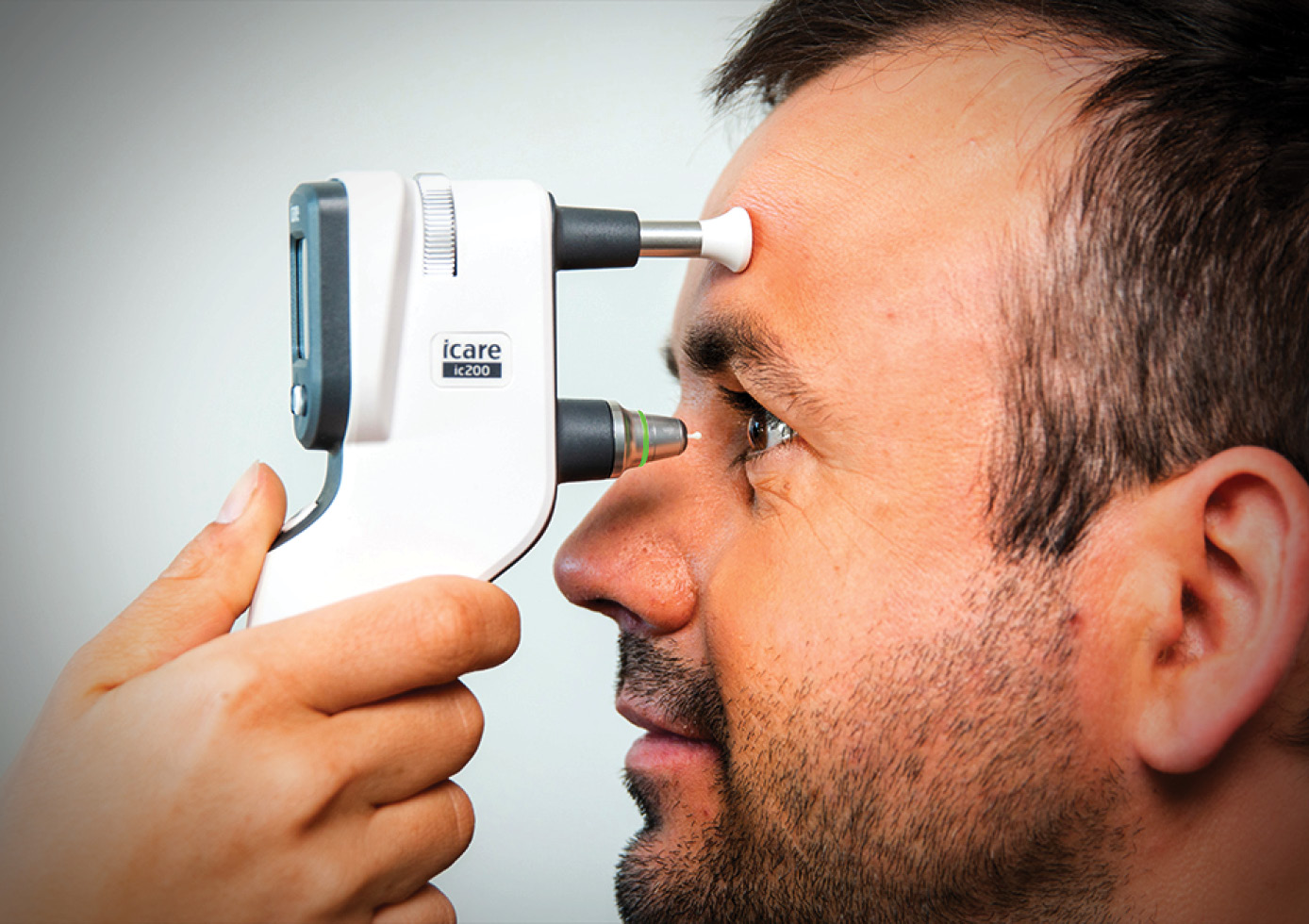
Early detection through routine screening is key.
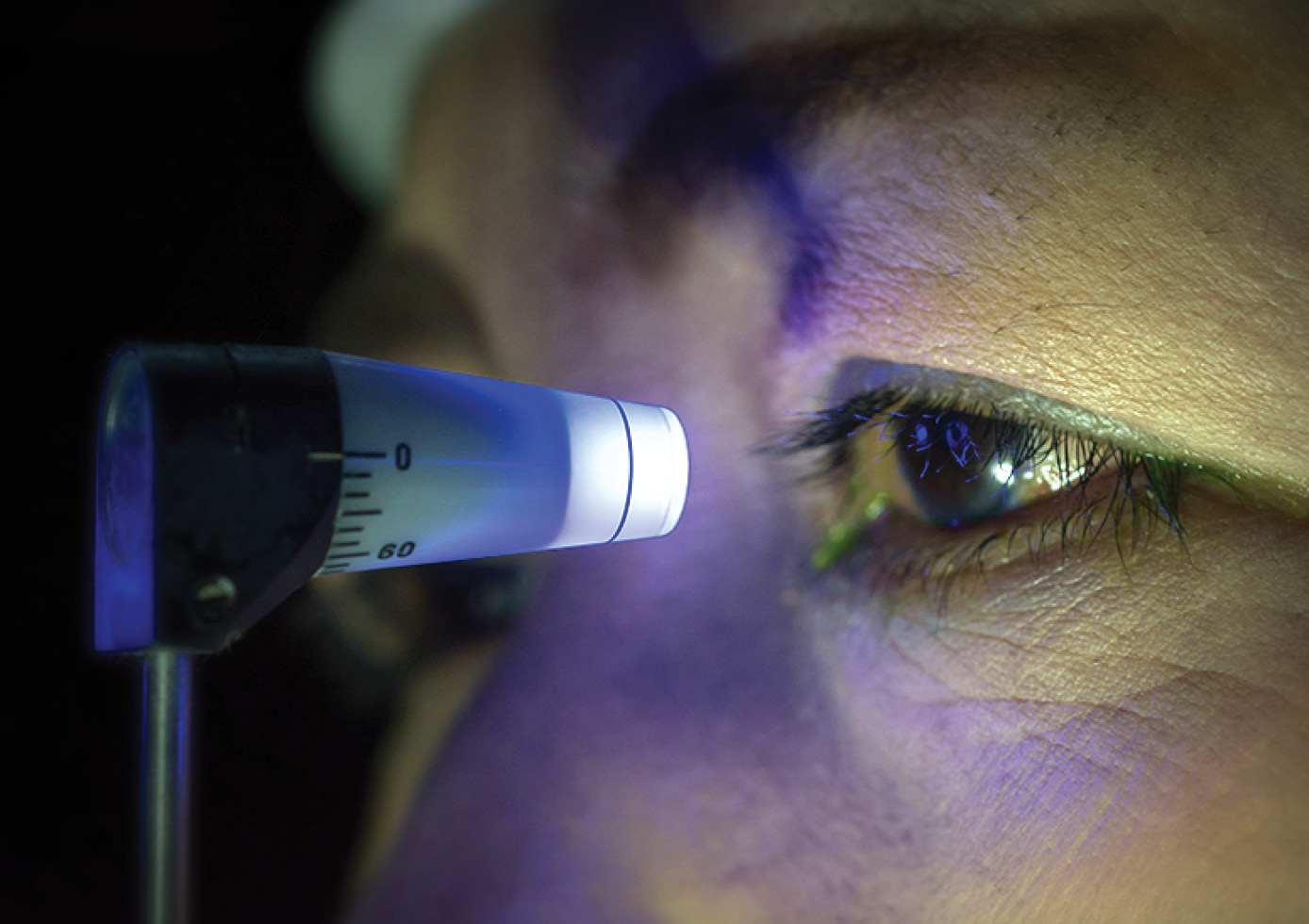
Glaucoma requires lifelong management to prevent vision loss.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
No, but it can be managed effectively to prevent further vision loss.
Adults over 40 or those with risk factors should have annual screenings.
If untreated, glaucoma can lead to irreversible vision loss.
Not always. Many cases are managed with medications or laser treatment, but surgery may be needed for advanced glaucoma.
Yes, managing stress, avoiding smoking, and controlling medical conditions support better eye health.

